The difference between outbound and inbound sales comes down to who makes the first move. Inbound pulls interested customers to you. Outbound pushes your message out to them. One earns attention; the other seeks it.
The real question is: do you need prospects to find you, or do you need to go find them?
Understanding The Core Difference In B2B Sales
Let's look at how the first conversation starts. One approach relies on being discovered. The other depends on direct, proactive contact.
Inbound sales works by attraction. You create helpful content like blog posts, webinars, or research reports. Your ideal customers find this content when they search for answers. This strategy establishes your company as a trusted authority. When a prospect realizes they have a problem, they already know your solution. By the time they talk to a salesperson, they are informed and interested.
Outbound sales is about taking the initiative. Your team identifies specific companies that match your ideal customer profile (ICP). Then, they reach out directly through cold calls, personalized emails, or LinkedIn messages. The goal is to start a conversation with someone who may not know your company exists or that they have a problem you can solve.
Inbound vs Outbound At A Glance
This table shows the core differences between the two methods. It gives a quick snapshot of each approach.
Characteristic | Inbound Sales (Pull) | Outbound Sales (Push) |
|---|---|---|
Initiation | The customer reaches out after finding your content. | Your sales team contacts a targeted prospect directly. |
Communication | Two-way and conversational, guided by the customer's needs. | One-to-many, focused on delivering a specific message. |
Customer State | Prospect is actively looking for a solution and is problem-aware. | Prospect is often unaware of the problem or your solution. |
Primary Goal | To educate, build trust, and guide prospects to a solution. | To create awareness, book a meeting, and qualify interest. |
This isn't just a sales theory. It reflects broader market trends. For instance, projections for Brazil's travel industry show a surge in outbound movement, with an estimated 15.4 million trips expected by 2028. That’s a 35% jump from 2018. This proactive "outbound" activity outpaces inbound tourism. It shows how a targeted, push-first strategy can create its own momentum. You can find details in Brazil's market dynamics and trade profile.
Understanding this fundamental difference helps you decide which strategy—or combination—is right for your team.
Comparing Practical Sales Strategies and Tactics
Let's move from theory to real-world actions. Each approach uses different channels and tactics to reach potential customers. Knowing these differences helps you build a sales playbook that works.
Inbound creates value first. The goal is to attract buyers by being helpful. You establish your company as the go-to expert before a sales call ever happens. It is a patient, educational process.
Outbound is built on direct engagement. You identify and connect with ideal customers who fit a specific profile. Often, they have not even started looking for a solution. This requires persistence and a clear value proposition.
This diagram shows the core philosophies. Inbound pulls customers in. Outbound pushes the message out.
As you can see, inbound relies on the pull of valuable content, while outbound starts conversations directly.
A Look at Inbound Tactics
Inbound marketing and sales tactics draw prospects toward you. They solve problems and answer questions, which builds trust over time.
Here are common inbound workflows:
SEO-Driven Content Creation: Write blog posts and guides that rank for terms your customers use. For example, a SaaS company might write "How to Reduce Customer Churn" and introduce its software as a solution.
Educational Webinars: Host live sessions that teach your audience something useful. This positions your team as experts and generates a list of qualified leads.
Lead Nurturing Sequences: Use automated email workflows to guide prospects. If someone downloads your ebook, they get follow-up emails with related content, slowly introducing your product.
The inbound sales cycle is often longer. But it delivers more educated and qualified leads. When a prospect speaks to a sales rep, they already understand their problem and trust your brand.
This approach works for businesses in established markets where buyers actively research solutions. It is a long-term investment that builds a reliable lead generation engine.
Breaking Down Outbound Strategies
Outbound creates opportunities from scratch. It is a direct approach that requires precise targeting and a compelling message to grab attention.
Here are actionable outbound workflows:
Multi-Channel Outreach Cadences: Build a sequence of touchpoints across email, phone, and social media. A simple cadence could be:
Day 1: Personalized email.
Day 3: Follow-up phone call.
Day 5: LinkedIn connection request with a short note.
Value-Centric Cold Calling: Focus call scripts on a prospect's potential pain points. Instead of saying, "We sell CRM software," a rep might ask, "Many sales leaders struggle with inaccurate pipeline data. Is that a challenge for you?" For more on this, check out these sales prospecting techniques.
Targeted Account-Based Marketing (ABM): Focus sales and marketing on a list of high-value accounts. For an enterprise software company, this could mean creating a custom demo and sending a direct mail package to decision-makers at one target company.
Inbound is a marathon, focused on building brand authority over time. Outbound is a series of sprints designed to start conversations now. Many companies blend both. They use inbound for a consistent flow of leads and outbound to target their most valuable potential customers.
Structuring Your Team For Inbound And Outbound Success
Your sales goals shape your team. You need the right people in the right roles. The skills for a great inbound rep differ from what an outbound rep needs. Asking one person to master both often leads to burnout and missed targets.
An Inbound Sales Representative acts as a guide. They connect with people who have already shown interest—they downloaded an ebook or requested a demo. These leads are warm. The rep's job is to listen, diagnose challenges, and show how your product is the solution.
An Outbound Sales Development Representative (SDR) is a hunter. They contact cold prospects who may not realize they have a problem. This role requires resilience, research skills, and the ability to create interest in seconds.
Getting this distinction right is critical. It influences everything from the first touchpoint to the handoff to an Account Executive.
Core Competencies for Each Role
The ideal skill sets for these roles are different. Matching the right talent to the right motion builds an efficient sales machine.
An Inbound Sales Rep must excel at:
Active Listening: The prospect is already talking. The rep's main job is to listen for pain points, goals, and buying signals.
Consultative Selling: They ask smart questions to diagnose a prospect's needs and build a solution together.
Product Expertise: Educated buyers ask tough questions. Inbound reps need deep product knowledge to run effective demos and handle queries.
A top-tier Outbound SDR needs to master:
Persistence and Resilience: Rejection is part of the job. They must stay motivated and keep making contact.
Research and Personalisation: Great outbound reps research a prospect's company, role, and industry to craft relevant messages.
Concise Value Communication: They have seconds to earn attention. They must state a compelling value proposition quickly and clearly.
The core difference is mindset. An inbound rep solves an existing need. An outbound rep finds a problem and creates an opportunity.
Building Your Team Structure
How you organize your team depends on your company's stage. A startup's structure looks different from a mature enterprise's. Here are a few common models.
The Startup Model (Founder-Led Sales)
At the start, founders often handle both inbound and outbound. This is a practical way to begin but is not sustainable. The main goal is to find which approach generates early traction.
Structure: 1-2 Founders do everything.
Workflow: Founders handle inbound demo requests and run their own outbound email campaigns. It is a manual process focused on learning what works.
Goal: Validate the Ideal Customer Profile (ICP) and find a repeatable sales process.
The Growth Stage Model (Specialised Roles)
Once leads come in steadily, it’s time to specialize. Split your inbound and outbound functions to maximize results. You can learn more about specific duties in our guide on the difference between an SDR and inside sales.
Inbound Team:
Marketing: Generates leads through content, SEO, and ads.
Inbound Sales Rep (or BDR): Qualifies these marketing-generated leads (MQLs) and books discovery meetings.
Account Executive (AE): Runs demos and closes deals.
Outbound Team:
Outbound SDR: Researches accounts, builds contact lists, and executes cold outreach to book meetings.
Account Executive (AE): Runs discovery calls and closes deals sourced by the SDRs.
This separation of duties is a game-changer. It allows each person to become an expert in their role. SDRs focus on generating meetings. AEs concentrate on closing deals. The result is a more efficient and predictable pipeline.
Choosing The Right KPIs To Measure Performance
If you cannot measure it, you cannot improve it. This is true in sales, but you cannot use the same dashboard for outbound and inbound. Tracking them with the same KPIs is like using a map of London to navigate São Paulo—it will not work.
For inbound sales, focus on efficiency and engagement. These leads are already interested. Your metrics should show how well you convert that interest into revenue. You measure the quality of your pull.
With outbound, the focus shifts to activity levels and outreach effectiveness. You are creating demand. You track the impact of your push.
Key Inbound Sales KPIs
Inbound metrics show the health of your marketing funnel. They show how well your sales team handles buyers who have already done research. The core question they answer is: "How well are we converting the interest we've earned?"
Here are the vital metrics to track:
Marketing Qualified Leads (MQLs): The total number of leads from your content and marketing activities. This is the top of your sales funnel.
MQL-to-SQL Conversion Rate: The percentage of MQLs your sales team accepts as Sales Qualified Leads. A low number here signals a disconnect between marketing and sales.
Lead-to-Close Rate: The percentage of qualified leads that become customers. This tests your team's closing ability.
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): The total cost of marketing and sales divided by the number of new customers. A good inbound strategy aims to lower this number over time.
A high MQL count with a low MQL-to-SQL conversion rate indicates a broken funnel. It usually means your marketing attracts the wrong audience, wasting budget and the sales team's time.
Tracking these conversion and cost metrics is essential to scale your inbound engine.
Essential Outbound Sales KPIs
Outbound is a numbers game, but it must be a smart one. The right KPIs measure how effective activity is, not just how busy your SDRs are. They answer the question: "Are our efforts reaching the right people with a message that works?"
Here are the core metrics for outbound leaders:
Activity Volume: The raw number of calls made, emails sent, and social media messages sent.
Response Rate: The percentage of outreach that gets a reply (positive or negative). A rate below 2-3% may indicate a problem with targeting or messaging.
Meeting Booked Rate: The percentage of prospects who agree to a discovery meeting. This KPI directly measures an SDR’s ability to create interest.
Pipeline Velocity: How quickly deals move through the sales pipeline, from the first meeting to a closed deal. A slow velocity can point to friction in your sales process.
These different dynamics appear in other industries, too. In 2024, Brazil's outbound travel market saw 12.8 million international trips, an 18.5% increase from the previous year. In contrast, inbound tourism was only 6.65 million visitors. This shows how a proactive, outbound-focused market can create its own momentum. You can read more about Brazil's international travel marketing dynamics to see the data.
Core KPIs For Inbound vs Outbound Sales Teams
You need a clear way to see how these metrics line up. The right KPIs track progress and tell a story about where your strategy is winning or failing.
Here is a breakdown of the most critical metrics for each sales motion.
Metric Category | Inbound Sales KPIs | Outbound Sales KPIs |
|---|---|---|
Top of Funnel | Marketing Qualified Leads (MQLs) | Activity Volume (Calls, Emails, Social Touches) |
Qualification | MQL-to-SQL Conversion Rate | Positive Reply Rate / Contact-to-Meeting Booked Rate |
Pipeline Health | Sales Cycle Length | Pipeline Velocity |
Closing Efficacy | Lead-to-Close Rate | SQL-to-Close Rate |
Financial Health | Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) | Cost per Opportunity / Cost per Acquisition |
Overall Success | Revenue from Inbound Sources | Revenue from Outbound Sources |
By tracking these KPIs separately, you get a clear picture of each engine's performance. It is the only way to diagnose problems and make data-driven decisions.
Deciding When To Use Inbound vs Outbound
Choosing between inbound and outbound is a strategic decision. It must be tied to your business model, market maturity, and goals. The right choice depends on your context. What works for one company could fail for another.
This is a practical framework. Look at your product's complexity, average contract value (ACV), and growth stage. This helps you build a sales motion that delivers predictable results. The goal is not to pick a side in the "outbound vs inbound" debate. It is to create a hybrid strategy that fits your situation.
When To Prioritise Outbound Sales
Outbound sales creates market momentum. It works best when your target customers are not actively searching for a solution. This may be because your product is new or they do not realize a better way exists.
You should lean on outbound if:
You have a high Average Contract Value (ACV). When a deal is worth tens of thousands, the resource-intensive nature of outbound is justified. You can invest time in researching and personalizing outreach for high-value accounts.
You are entering a new market. You cannot wait for prospects to search for you if they do not know you exist. Outbound lets you educate the market, introduce your solution, and get early revenue and feedback.
Your Ideal Customer Profile (ICP) is narrow. If you sell to a small, defined group, like CTOs at fintech companies, outbound is more efficient. You can build a target list and contact them directly.
An early-stage company selling complex cybersecurity software to banks is a good example. Their buyers are not searching for "new security platform." They need to be shown the risk and presented with a tailored solution.
Outbound gives you control over your pipeline. Instead of waiting for leads, you dictate the volume and timing of your outreach. This is a powerful tool for hitting short-term revenue goals.
When To Focus On Inbound Sales
Inbound sales works well when your buyers are aware of their problem and actively looking for information. It is a long-term strategy that builds a cost-effective lead generation engine. It positions your company as a trusted authority.
You should invest in inbound when:
You operate in a competitive, established market. When buyers search for solutions like yours, the best way to win is to be the most helpful resource. SEO-driven content and webinars capture this existing demand.
Your product has a lower ACV and a shorter sales cycle. For more transactional sales, inbound is scalable. A single blog post can generate leads for years, which lowers your Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC).
Your solution addresses a widely understood problem. If your ICP is broad and their pain points are common, content is an efficient way to reach them. You can attract prospects by answering their questions.
A business selling project management software operates in a crowded space. Inbound content like "Best Project Management Tools for Remote Teams" attracts qualified buyers who are already evaluating options.
The Diagnostic Checklist For Leaders
To determine your strategy, ask yourself some key questions. Your answers will show whether an outbound-heavy or inbound-heavy approach—or a blend of both—is the right fit.
Is our ideal customer actively searching for a solution like ours? (Yes = Inbound; No = Outbound)
What is our timeline for generating pipeline? (Short-term = Outbound; Long-term = Inbound)
Is our Average Contract Value high enough to support personalised outreach? (Yes = Outbound; No = Inbound)
Are we educating a new market or competing in an existing one? (New = Outbound; Existing = Inbound)
How large and defined is our target audience? (Narrow = Outbound; Broad = Inbound)
This analysis is relevant on a global scale. Brazil's international remittance flows show a large outbound market at US$3.06 billion in 2024, projected to hit US$4.76 billion by 2028. This activity reflects residents sending money abroad for investments—a clear signal for sales teams to target these clients with an outbound strategy. You can find more insights on Brazil's international remittance market on ResearchAndMarkets.com.
Answering these questions honestly provides a blueprint for an effective sales engine.
Integrating Your Sales Motions With Samskit
Whether you use outbound, inbound, or a hybrid model, the goal is the same: get clean, reliable data into your CRM to make better decisions. The problem is that data from a cold discovery call differs from data from a warm inbound demo.
You need a way to standardize how you capture insights. The right tool can bridge this gap. It ensures every customer conversation is captured, analyzed, and used to build a complete picture in your CRM.
Creating A Single Source Of Truth
This means you automatically record and pull insights from every call, whether it is an inbound demo or an outbound prospecting call. For inbound leads, this captures the nuances of a conversation with an informed buyer. It ensures a smooth handoff to an Account Executive.
For your outbound reps, it provides a clear view of what works. Which opening lines are effective? What objection-handling techniques fail? This is about seeing what is happening, without manual data entry.
Here’s how a tool can break down call data, flagging items like competitor mentions and syncing them to your CRM.
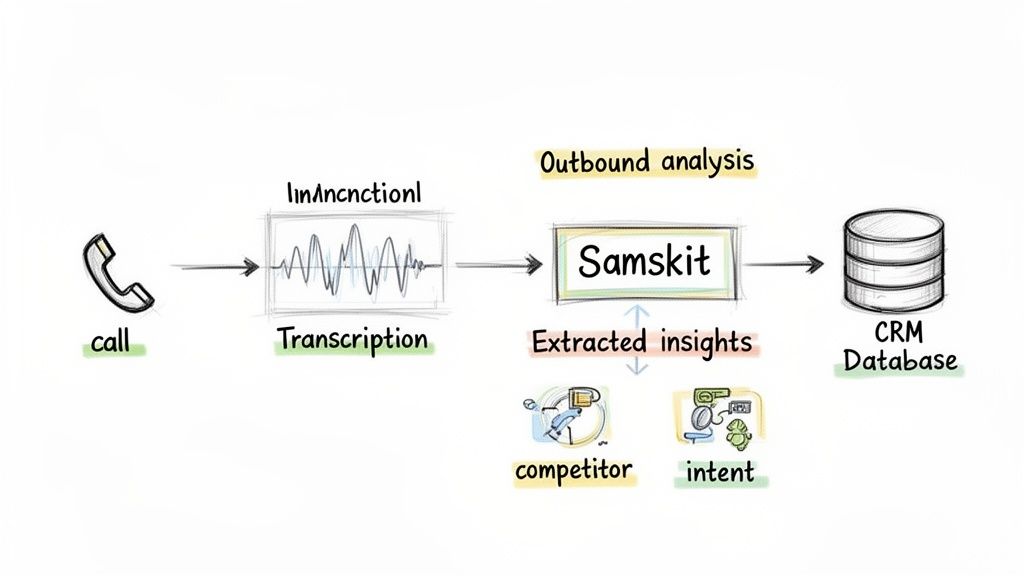
Automating this insight capture means important deal intelligence does not get lost, regardless of how the conversation started.
A Simple, Repeatable Integration Workflow
Getting your inbound and outbound data on the same page does not require a complete process overhaul. The focus should be on smart automation that saves reps time and gives leaders trustworthy data.
It comes down to a simple, three-step workflow:
Automated Call Capture: A bot joins, records, and transcribes every sales call—from both inbound and outbound teams—on platforms like Zoom, Google Meet, and Microsoft Teams.
Intelligent Analysis: The transcript is analyzed to pull out key information: competitor mentions, buyer intent signals, budget discussions, and next steps.
CRM Synchronisation: This structured data is automatically pushed to the right fields in your CRM. The deal stage is updated, notes are added, and next steps are logged without the rep doing any manual work.
This simple process saves each rep hours of admin work every week. More importantly, it gives leadership clean, consistent data across the entire sales organization. This leads to more accurate forecasting and coaching tied to actual performance.
By automating how you capture and analyze every conversation, you create a powerful feedback loop. You can learn more about how Samskit turns customer meetings into reliable CRM updates and supports both inbound and outbound teams. This integration ensures your strategy is built on what customers say, not on patchy CRM data.
Frequently Asked Questions
Let's address common questions sales leaders have when comparing inbound versus outbound. Here are straightforward answers to help you build a smarter sales strategy.
Can A Company Succeed Using Only One Sales Strategy?
It is possible, especially for startups, but it is rarely the best path. Most businesses find a hybrid model delivers more sustainable success.
Relying only on inbound can be slow and unpredictable. Going all-in on outbound is often expensive and hard to scale.
The best results come from blending the two. Inbound creates a steady stream of cost-effective leads. Outbound lets you target high-value accounts with precision. This combination gives you both long-term sustainability and direct pipeline control.
Which Strategy Has A Better Return On Investment?
This depends on your time horizon.
Outbound often shows a faster ROI in the short term. You can start a campaign and have meetings booked within weeks. It is direct and immediate.
Inbound is a long-term asset. A single great blog post can generate leads for years. This ultimately drives down your customer acquisition cost (CAC) and delivers a higher ROI over time. A smart strategy balances quick wins from outbound with the compounding value of inbound.
The debate is not about which one is "better." It is about finding the right balance for your company's stage and goals. Outbound fills the pipe now; inbound ensures it stays full for years.
How Long Does It Take To See Inbound Sales Results?
With inbound, patience is required. You should plan for 6 to 12 months of consistent effort in content creation and SEO before seeing a predictable flow of quality leads.
The results are cumulative. The longer you continue, the more powerful your lead generation becomes. An outbound campaign gets you meetings this week, but it stops when you stop. A good inbound funnel works for you 24/7.
How Does Technology Help A Hybrid Sales Team?
Technology holds a modern hybrid team together. Without it, you have data silos and a disjointed customer view. A tool like Samskit is essential here. It automatically captures and standardizes data from every customer conversation, whether it was an inbound discovery call or a cold outbound pitch.
This means your CRM data is clean, complete, and reliable. For sales managers, this provides a single source of truth for coaching and strategy. You can get a clear picture of what works across the entire customer journey for both inbound and outbound motions.
By automating call analysis and CRM updates, Samskit gives your sales team a unified view of every customer interaction. This saves reps hours of admin time and provides leaders with the clean data needed to scale both outbound and inbound efforts effectively. Learn more at https://samskit.com.
